This transformer is Dyn1, or this transformer vector group is Dyn1. Have you heard it? If yes, then what does it mean? Today, I will discuss what a transformer vector group is and its importance in power systems.

What Is A Transformer Vector Group?
The transformer vector group is nothing but the physical connection of a phase transformer. From the vector group, we can determine the number of transformer windings, the connection of each winding(star, delta, or zig-zag), and the phase shift between the windings. The vector group varies for the ways of Delta and Star winding connections and polarity.
Our other articles you may like.
- Transformer Differential Protection and how it works
- How Circuit Breaker Anti-pumping works?
- Pole discrepancy protection of a circuit breaker.
What Does The Vector Group Symbol Mean?
Meaning of Dyn1 Vector Group
Let’s start with Dyn1. This is a two-winding transformer vector group.
The capital D means the high voltage winding is delta-connected. Small y means the low voltage side is y-connected or star-connected. The small n means the star winding is solidly grounded.
Now, what is the meaning of the number 1? The number is used to indicate the phase shift.
Phase shift is calculated with reference to the high voltage side. Actually, the number indicates the position of winding in a clock. The reference winding is considered as zero. Then the other winding is placed according to the number.
If I place it in a clock, then it looks:
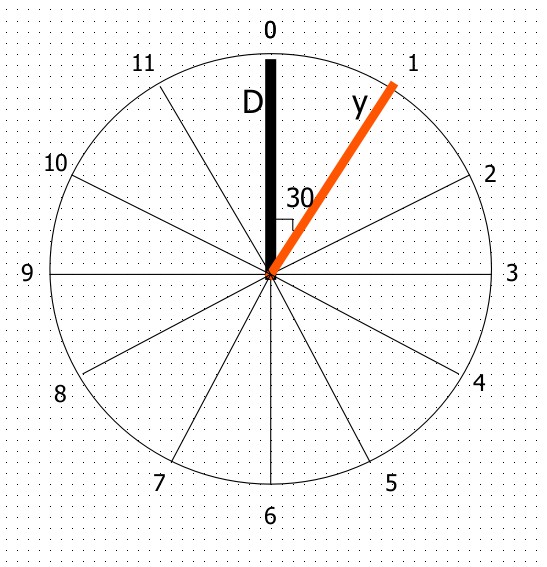
Here, the Delta winding is in zero position, and the y winding is in position 1. Phase difference between two corresponding positions is 30 degrees. Since the Y winding is placed at the 30° clockwise position, the Y voltage lags the Delta voltage by 30°. That means if the phase angle of the Delta winding R phase is 0, then the star winding r phase voltage angle will be -30°. This 30° lag also occurs in the Y and B phases also.
Understanding Vector Group Dyn11
Dyn11 is almost the same as Dyn1 except for the number. Here the number is 11. So, the star winding is at position 11, keeping Delta at zero position.
This time the figure will be:
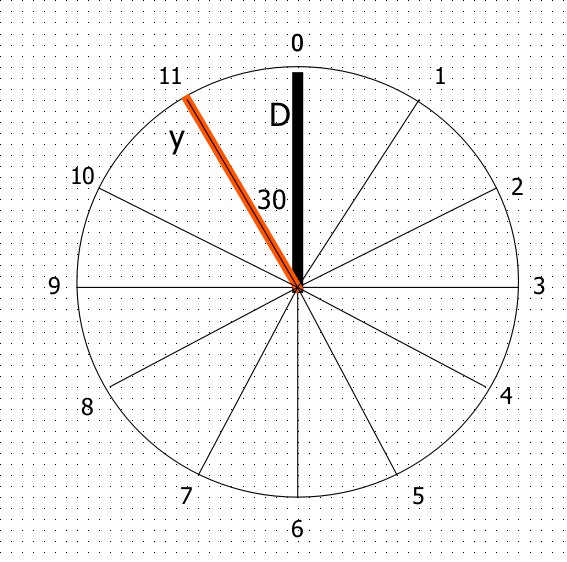
Now, the star winding is 30° left of the delta winding. So, the star winding leads the delta winding by 30°.
Transformer Vector Group Of a Three-Winding Auto Transformer
The most common autotransformer vector group is YNa0d1. Here, Y means the primary high voltage winding is star-connected. The ‘a0’ means an autotransformer with zero degree phase displacement. That means the secondary middle voltage winding is also star-connected. And finally, d1 means the tertiary winding is delta-connected with 30° phase lag with the primary side.
Frequently Asked Questions On Transformer Vector Group
What is a transformer vector group?
A transformer vector group describes its winding connections and phase displacement.
Where can I get a transformer vector group?
You can get it from the transformer nameplate. Every transformer nameplate holds its vector group.
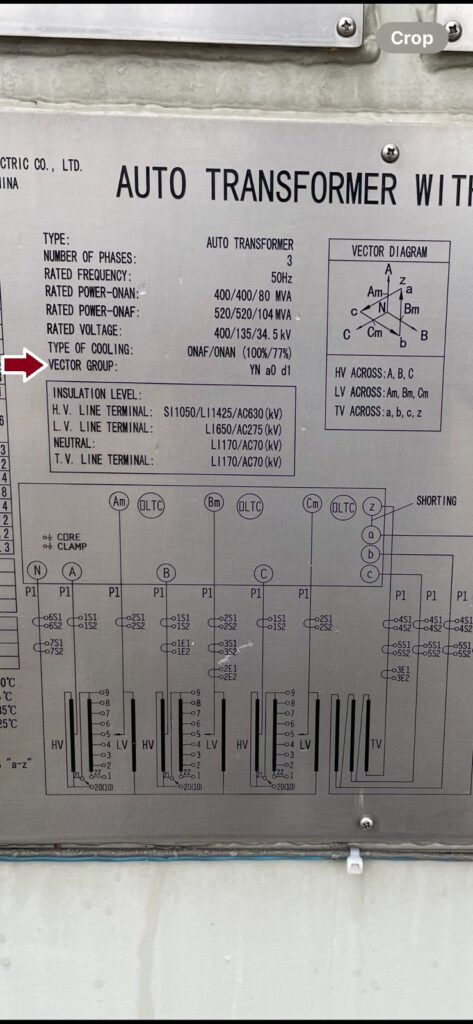
What does a transformer vector group indicate?
A transformer vector group indicates its winding connection and phase shift.
What is the phase displacement of the Dyn1 transformer?
The phase displacement is 30° lag in star winding.
Why is the transformer vector group important?
It is important for differential stability protection, parallel operation, and protection coordination.
What do the letters in a transformer vector group mean?
The letter indicates the winding connection type. For example, D means delta winding connection, and y means star connection. Capital letter used for the high voltage side and small letter used for the low voltage side.
What does the number in a vector group indicate?
The number indicates the phase displacement between the primary and secondary winding.
What is the difference between Dyn1 and Dyn11?
The only difference between Dyn1 and Dyn11 is phase displacement. In Dyn1 LV star winding lag HV delta winding by 30°. Whereas, Dyn11 LV star winding leads HV delta winding by 30°.
Today, I have tried to provide the main theme of the vector group. Later, we will discuss the winding connection and differential stability condition for each vector group.
Thanks for your reading.
