Since you are visiting my site, I assume you are familiar with the pole discrepancy. But do you know how pole discrepancy works in a circuit breaker?
If you have a clear understanding of pole discrepancy and its circuit diagram, then this post is not for you. But if you have no idea or have doubts about pole discrepancy, then I think this post will help you to clear your understanding.
Read More Posts on This Site
What Is Pole Discrepancy?
In high voltage, a three-phase circuit breaker should operate(open or close) all three phases at the same time. If one or two poles lag or fail to move, then it creates a pole discrepancy fault.
A pole discrepancy relay is used to overcome a pole discrepancy fault.
How Pole Discrepancy Protection Works in a Circuit Breaker?
A pole discrepancy relay continuously monitors the status of each pole auxiliary contact. If the relay detects that one or two poles remain open or closed more than the set time( for example, 3-4s) after the others. It defines this as a pole discrepancy fault.
If a pole discrepancy is detected, then the pole discrepancy relay sends a trip command to open all phases completely.
Understanding Circuit Diagram of Pole Discrepancy Protection
Earlier, I already said that if the pole discrepancy relay detects phase mismatch, then it sends a trip signal to all phases.
In this section, I will discuss the circuit diagram of a pole discrepancy relay. How does it detect phase mismatch? And how does it send the trip command?
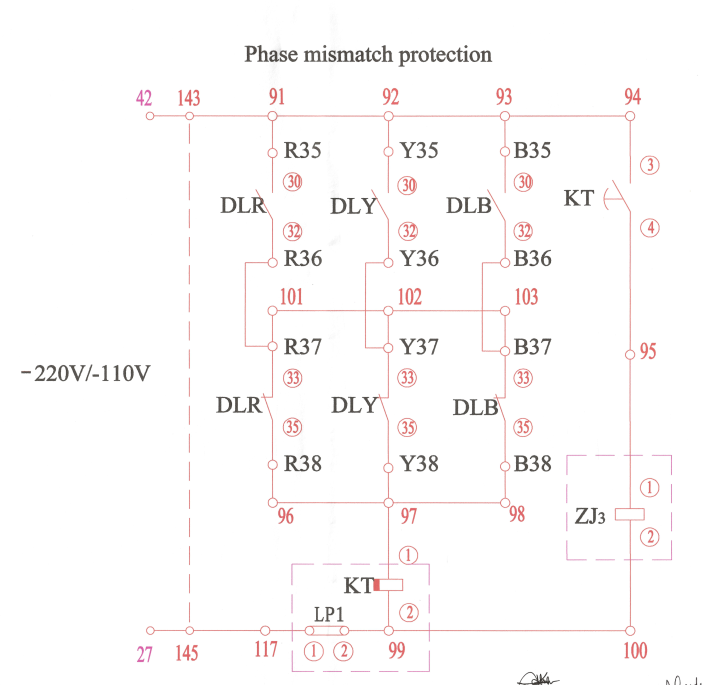
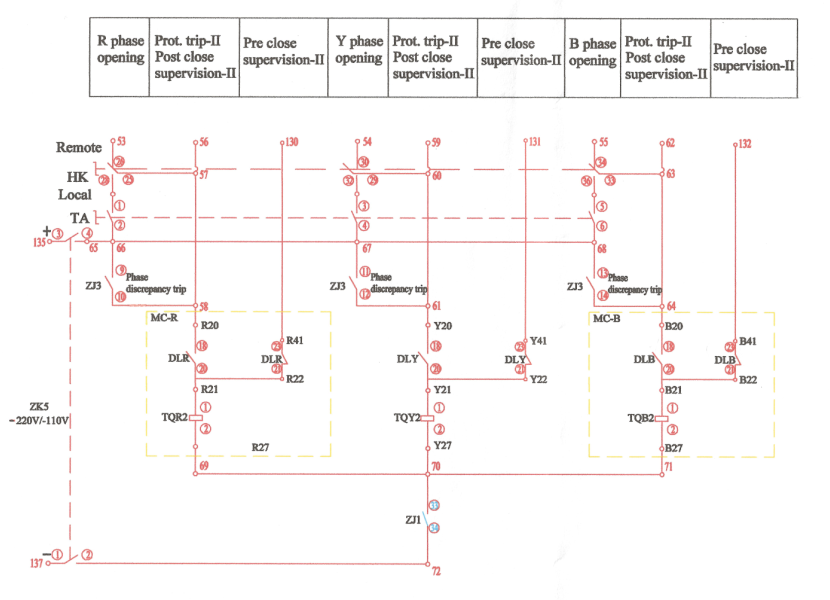
This drawing shows how a pole discrepancy relay detects a pole discrepancy condition.
First, know the meaning of the component code.
Here, KT means pole discrepancy relay(between points 97 and 99) and contact(between 94 and 95).
ZJ3 is open phase relay.
And, DL are breaker auxiliary contacts. DLR for phase R, DLY for phase Y, and DLB for phase B. The above three contacts(between 30 and 32) are normally open contacts, and the lower three contacts(between 33 and 35) are normally closed.
Suppose phase R and B are open, and phase Y is not open(closed). Then the above DLY(Y35 & Y36) contact will make, and DLR(R35 & R36) and DLB(B35 & B36) will remain open, like the figure below.
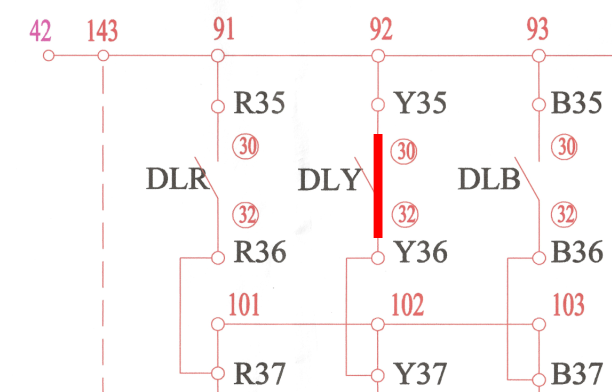
Now, the points 91, 92, 93, 101, 102, 103 are short, and positive voltage is at 101, 102, 103 through DLY.
On the other hand, the below normally closed DLY contact will be open as the Y phase is closed. But other normally closed contacts, DLR and DLB remain closed. Then the figure looks like below.
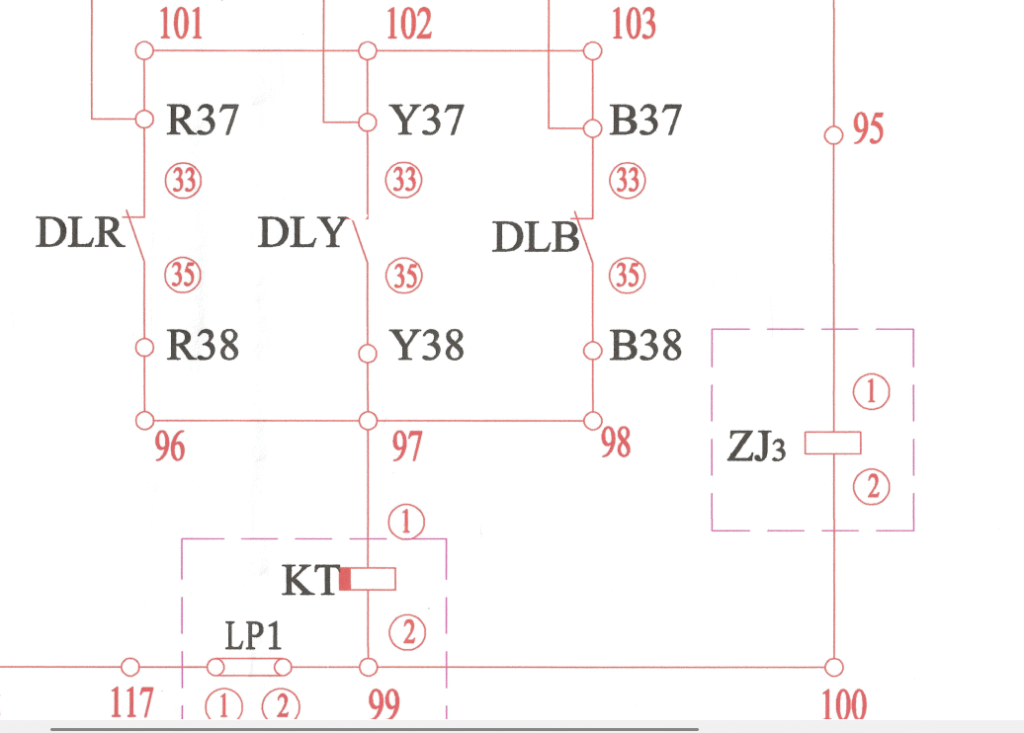
So, the positive voltage will be present at points 96, 97, 98 through path DLR and DLB.
The whole figure at this condition will look like:
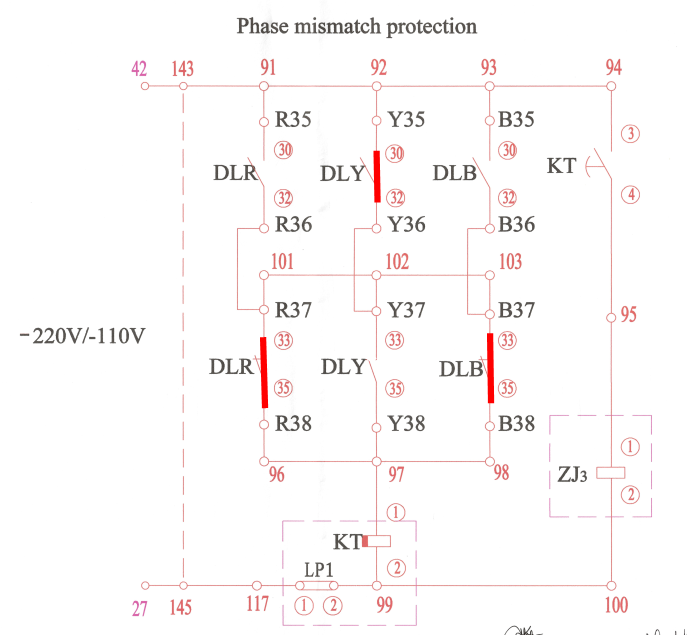
Now, the pole discrepancy relay KT is energized by a positive voltage at point 97 and a negative voltage at point 99. It has a set timer(for example, 3s or 4s).
When the pole discrepancy relay (between 97 and 99) is energized, and expires the time delay. It closes the contact KT (between 94 & 95). Then the open phase relay ZJ3 energizes, and it will send a trip command to three phases.
Now, I will discuss how ZJ3 sends a trip command.
When a pole discrepancy occurs, then ZJ3 is energised and closes the ZJ3 contact. Then the drawing will be:
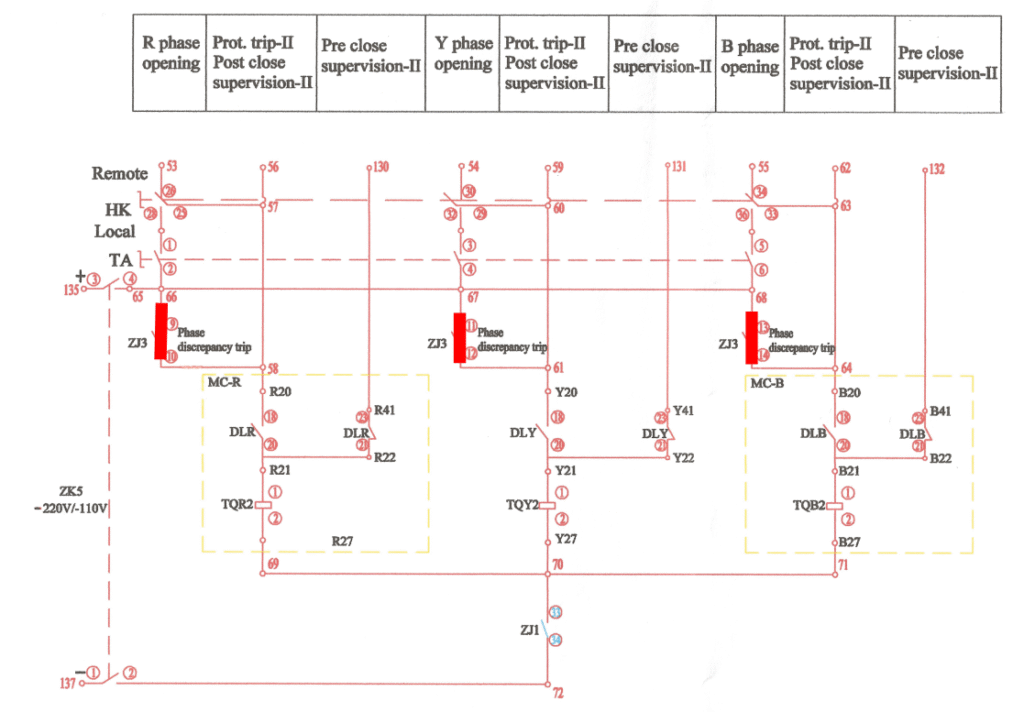
I have already discussed DLR, DLY, and DLB. TQ indicates breaker trip coil, R for phase R. If ZJ3 makes and the breaker of any phase is closed, then DL of that phase also makes contact, and trip coil TQ gets energised. That’s how the mismatch phase gets opened.
This scenario happens for any kind of phase mismatch, like phase R open and the other two phases closed, then the pole discrepancy relay will trip the other two phases.
Why Pole Discrepancy Protection is Important?
Circuit breaker pole discrepancy protection is very important for the power system. Because Phase mismatch can create an unbalanced current in a three-phase system. Besides, it can damage the breaker contact and connected equipment. Also reduces system reliability and protection coordination.
Frequently Asked Questions On Pole Discrepancy Protection
Thanks for your readings. I hope this post adds some value to your engineering learning. I will try to integrate a video explanation on pole discrepancy tripping as soon as possible.

Pingback: Substation Commissioning Checklist: Step-by-Step Guide