Transformer differential protection is one of the major protection schemes of a power transformer. This high-speed protection scheme is used for 2 MVA and above power transformers.
In this post, I will try to describe what transformer differential protection is and how it works. I hope this post will help students and apprentices in the power system.
What Is Differential Protection?
From the word differential, we can imagine that it is a difference of something. Yes, differential protection works on the difference of current between the two sides of the transformer. There is no fault on the transformer; both sides’ currents are balanced, difference between both sides’ currents is zero. As a result, no differential protection is actuated.
But if there is any fault in the differential protection zone(the protection zone will be described later), this will give an imbalanced current. As a result, the difference will be more than zero, and the differential protection will operate.
Differential Protection For a Single-Phase Transformer
This is only for example purposes, cause differential protection is never used in a single-phase transformer.
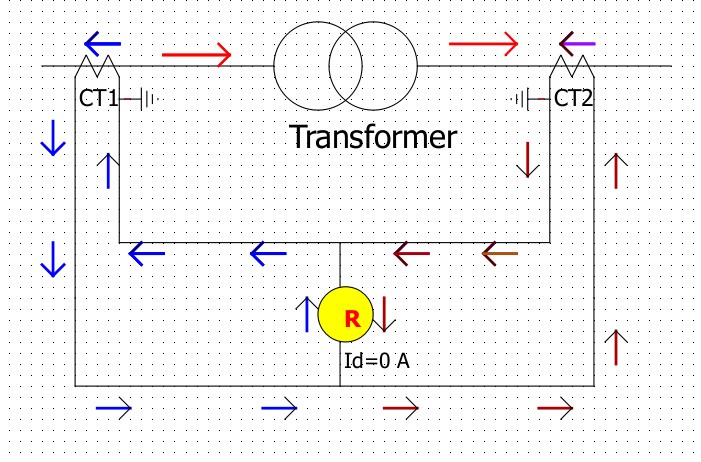
This is a simple drawing for single-phase transformer differential protection. The figure shows a normal(not faulty) condition. In normal conditions, current flows from the primary side to the secondary side.
Now we need to know a basic concept of CT(current transformer), CT polarity is set in such a way that the current in the secondary winding flows in the opposite direction to the current in the primary winding.
As current flows from left to right in the primary winding on both sides. The CT secondary current will flow from right to left for both CTs.
As current flows from the opposite direction in Relay R, the differential current Id=0. So, the relay will not actuate. This is called a balanced condition or differential stable condition.
When a fault occurs in the differential protection zone, the figure looks like below:
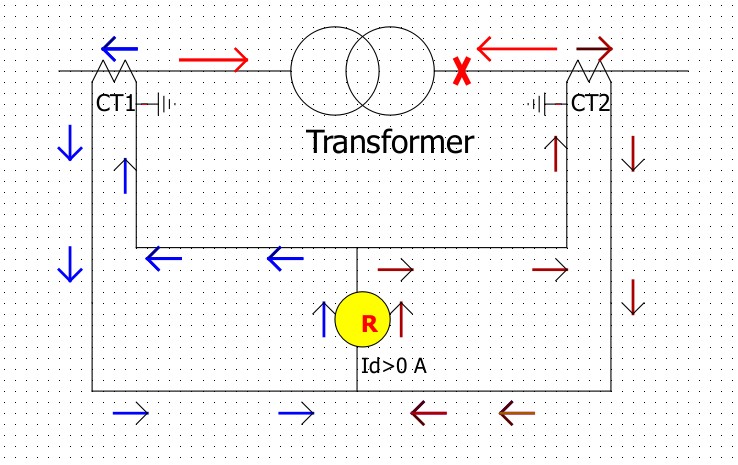
As current always flows into the direction of the fault. Now, transformer secondary side current flows from right to left (which is left to right direction in the upper figure). So, CT2 current will flow from left to right.
This time, CT1 and CT2’s currents enter the relay from the same direction. So the current that flows through the relay is the sum of CT1’s current and CT2’s current. This makes a sensitive value to actuate differential protection. Thus, it gives a differential protection trip. This scenario is called a differential unstable condition.
This is the basic concept of transformer differential protection. Though there are a few factors(such as vector group, transformer ratio, and CT ratio) to consider. I will discuss these factors in the next section.
Differential Protection For A Three-Phase DYn1 Transformer
Differential protection of a three-phase transformer is almost the same as single-phase transformer described above. The only difference is the three-phase CT arrangement. Transformer Delta side CT should be connected in a star arrangement, and transformer Y side CT should be connected in Delta. As a result, the phase angle shifts canceled each other.
The three-phase arrangement looks like:
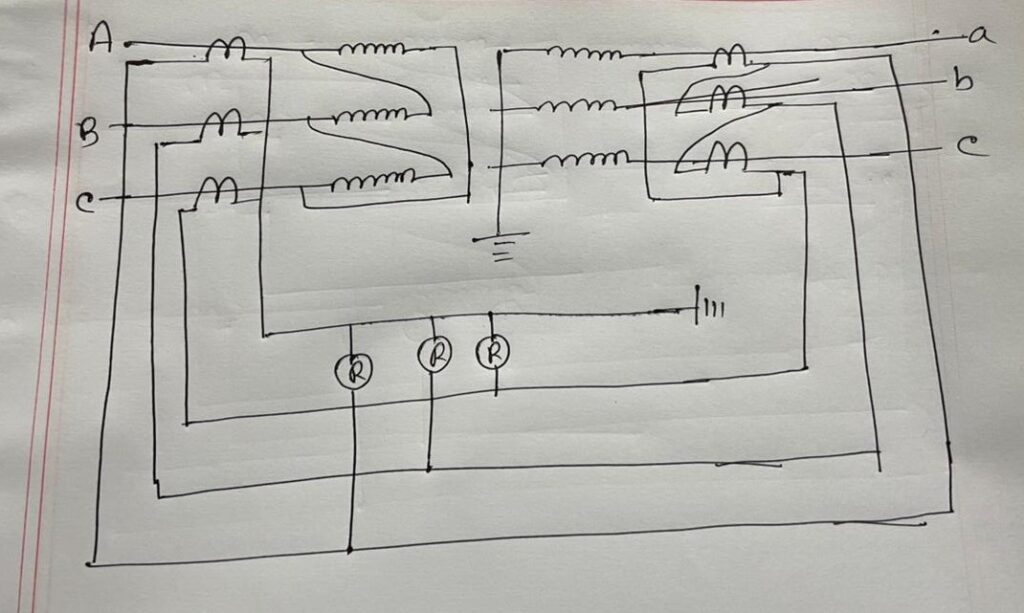
When a fault occurs between two CTs, differential current flows through the relay R. Which actuates differential protection. But if a fault occurs outside the CTs, zero differential current will flow through the Relay R. This time, no differential trip will activate.
The zone between the CT, which is connected to the relay, is called the differential protection zone. The CT may be taken from the transformer bushing CT or the post CT. Common practice is to use two differential relays for a transformer. One CT is taken from the bushing CT, and the other one is taken from the post CT.
Frequently Asked Questions on Transformer Differential Protection
What is transformer differential protection?
Transformer differential protection is a protective scheme that detects internal faults in a power transformer by comparing the current entering the transformer with the current leaving it.
What is differential protection zone?
The zone between two CTs connected to the relay is known as the differential protection zone. For the fault outside this zone, no differential protection is actuated.
Is the differential protection scheme used only for transformers?
No, differential protection is also used for parallel line protection.
Besides differential protection, what other protection is also used in a transformer?
Besides differential protection, transformers also use inrush blocking, overcurrent protection, overvoltage protection, restricted earth fault protection, and so on.
Which relay model is used for transformer differential protection?
7UT86(siemens), 7UT85, P643(micom), 7UT612
Thanks for your reading. I have tried to give a good touch on transformer differential protection.
You may read the substation commissioning checklist.

Pingback: Transformer Vector Group: Meaning, Types and Phase Shift
Pingback: Substation Commissioning Checklist: Step-by-Step Guide