The interlock of a circuit breaker, isolator, and earth switch is nothing but the operating sequence. This sequence is significant for a substation. Understanding the interlock of switchgear is the first duty for a substation operator.
In this post, I will discuss why interlock is important, interlock logic. Besides, how interlocking works in a substation.
Assuming you are familiar with what a circuit breaker, isolator, and earth switch are, we will begin the discussion.
Why is the Interlock of the Circuit Breaker, Isolator, and Earth Switch Important?
I have already mentioned that the interlock is the operating sequence of switchgear elements. A proper interlock system permits operation only if the specific condition is satisfied. It is a safety mechanism used in electrical substations to ensure that these devices are operated in a correct and safe sequence. Interlocking prevents incorrect operation that could lead to equipment damage, electrical faults, or danger to personnel.
Let’s look at an example. A circuit breaker is an online device. It can operate at rated live voltage and current. On the other hand, an isolator and earth switch are offline devices. The operation of the isolator and earth switch at the live line is very dangerous. Even if it can cause life hazards.
If an isolator is operated with both sides of voltage, it will create heavy sparking. If we connect the earth switch with a live line, then high voltage will be grounded. As a result, a very high short circuit current will flow through the earth switch. The connected equipment will be thermally damaged. A powerful arc flash can occur at the earth switch. This may be life-threatening.
Interlock Logic of Circuit Breaker
Circuit breaker interlock ensures that when a circuit breaker is allowed to open, and when a circuit breaker allowed to close.
A circuit breaker is always allowed to open except for circuit breaker trouble.
But the circuit breaker closing is not allowed at all times. Circuit breaker closing is permitted only according to the interlocking scheme.
Now, I will discuss the circuit breaker closing interlock for a double busbar system.
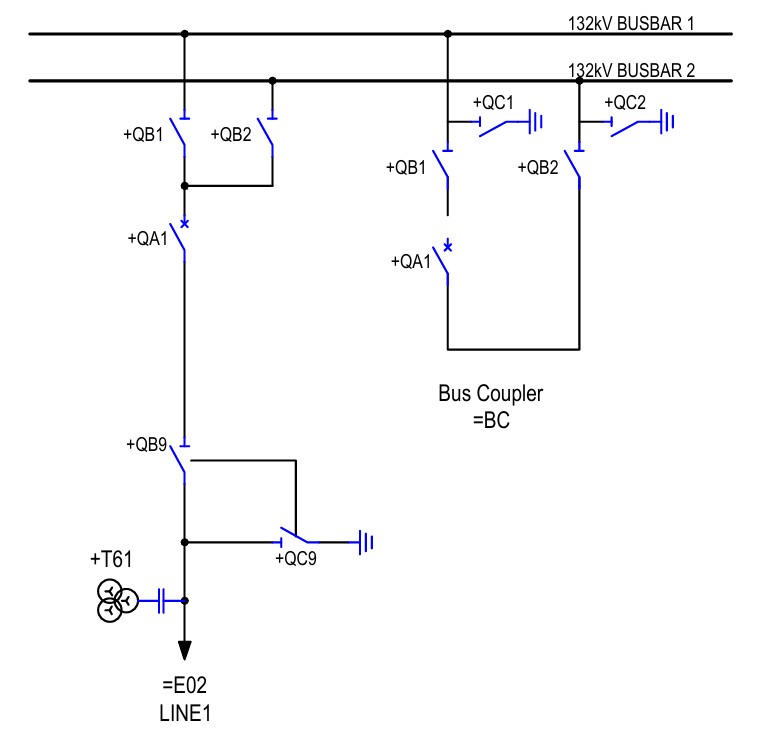
This is a single-line diagram of a line for a double busbar system. Here, +QA1 indicates a circuit breaker. +QB1 and +QB2 are the isolators for bus1 and bus2 respectively. +QB9 is the line isolator. +QC1 and +QC2 are the earth switches for bus1 and bus2 respectively. +QC9 is the line earth switch.
The closing interlock logic for the circuit breaker +QA1 is:
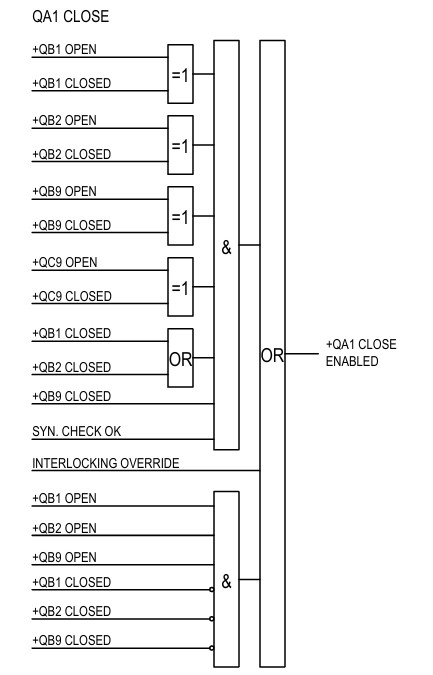
Now, try to understand the logic. The circuit breaker closing is enabled if the output of the upper AND gate is 1 or the interlocking override, or the output of the lower AND gate is 1.
=1 is the symbol of the XOR gate. It will be 1 when an odd number of inputs is 1 or TRUE. Since only two inputs are used here. So, its output will be 1 when any of the inputs is TRUE.
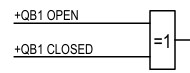
This output will be 1 when bus1 isolator +QB1 is at a definite position, open or closed. When the isolator moves from open to closed or closed to open, the output will be zero.
All XOR gate outputs will be 1 when all isolators and the earth switch are in open or closed position. The upper AND gate will be 1, if +QB9 is closed, any of +QB1 and +QB2 are closed, and all other isolators, sync voltage between line and bus within the range, and the earth switch are perfectly closed or open condition. Under this condition, the circuit breaker +QA1 is permitted to close.
If interlocking is overridden, then the circuit breaker will be closed without checking any conditions. Adequate precautions must be taken before overriding the interlock.
The lower AND gate will be one when all isolators are in open condition. This condition also allows the circuit breaker to close. This condition occurs during maintenance.
Read more articles on circuit breaker.
- Circuit Breaker Anti-Pumping Relay Working Principle
- How Pole Discrepancy Protection Works in a Circuit Breaker?
Circuit Breaker Closing Interlock Circuit
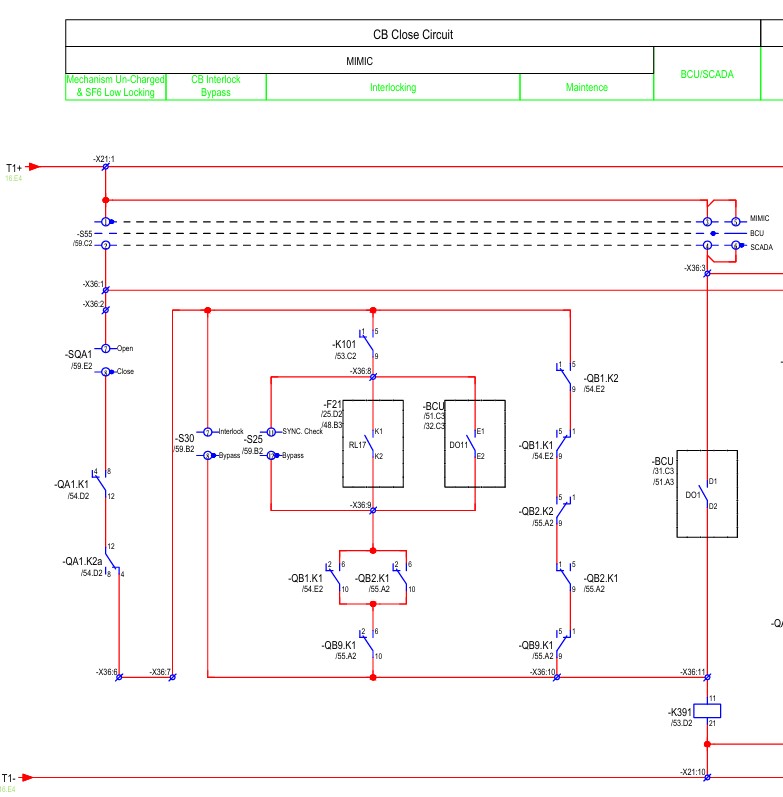
The coil -K391 is the coil to close the circuit breaker manually. If -K391 is energized, then the circuit breaker closing coil is also energized.
Here, -SQA1 is the circuit breaker open close switch from the mimic. -QA1.K1 is the contact of the circuit breaker spring charge. If the spring charge is normal, then the contact will close. On the other hand, QA1.K2a is the contact for the SF6 pressure of the circuit breaker. The contact will also close when the SF6 gas pressure is normal.
If the breaker spring charge and SF6 gas pressure are normal. Then coil-k391 can be energized by three paths from the mimic pulse.
One path is bypassing the interlock through -S30 switch. We should avoid this operation.
The second path is the interlock of normal operation. The contact -K101 ensures all isolators and earth switches are in definite positions. Then it checks the synchronisation condition. We can bypass it through -S25; such an operation is also discouraged. The protection relay and BCU can check the sync. condition parallelly.
If the sync. conditions are fulfilled, the positive voltage passes at -X36:9. -QB1.K1 and -QB2.K1 are the contacts of bus1 and bus2 isolator respectively. -QB9.K1 is the contact of the line isolator. If any of the bus isolator is closed and the line isolator is closed, then positive voltage will pass to -K391 through the mimic switch.
The third path for the maintenance condition. If all the bus isolators and line isolators are open, then positive pass to the coil -K391.
Operation from the BCU is not our main topic. So, we will discuss it later.
Isolator(DS) Interlock
Both the opening and closing interlocks of an isolator are the same. When a circuit breaker is permitted to close, it is also permitted to open at that condition.
Bus Isolator Interlock
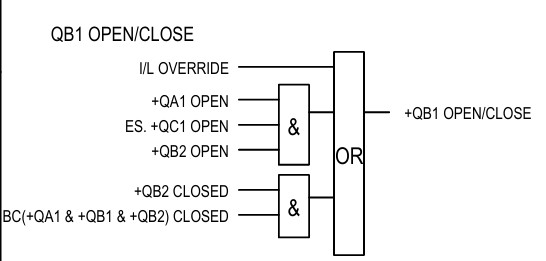
This is the interlock for QB1 bus1 isolator. This isolator is allowed to open/close at 3 different conditions.
Condition 1: if the interlock is overridden. Which is usually discouraged.
Secondly, if the circuit breaker(+QA1), bus 1 earth switch(+QC1) and bus 2 isolator(+QB2) are open. Then the bus 1 isolator +QB1 is permitted to close.
Thirdly, the bus coupler’s closed condition. If the bus coupler is closed, that means both isolators of the bus coupler and the circuit breaker of the bus coupler are closed. And the bus 2 isolator +QB2 is closed. Then it permits closing the bus 1 isolator +QB1.
The interlock of the bus2 isolator is almost the same of bus1.
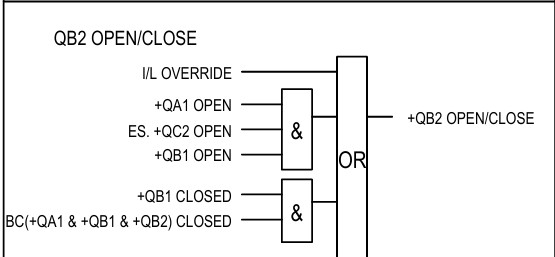
It is unnecessary to describe the logic for bus 2.
Line Isolator Interlock with Circuit Breaker and Earth Switch
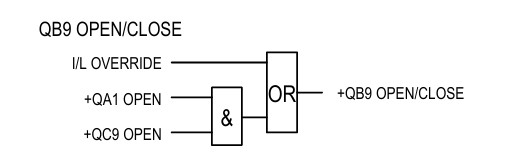
The line isolator is allowed to operate when the interlock is overridden. Or both the line circuit breaker and the line earth switch are open.
Line Earth Switch Interlock
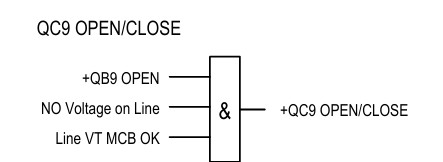
Line earth switch is permitted to open or close when the line isolator +QB9 is open, and no voltage in the line, and the line VT MCB condition is ok. Here, the Line VT MCB condition is added because if the line VT MCB is off or faulty. Then it shows no voltage in the relay or BCU for the live line. Which is very dangerous.
Frequently Asked Questions on Switchgear Interlock
What is the interlock of a substation?
The interlock of a substation is the operating sequence of the circuit breaker, isolator, and earth switch.
Why is the interlock very important for a substation?
Interlock ensures the safety of the equipment and the human being.
Can I open an isolator under any condition?
No, before operating the isolator, you must satisfy the required condition.
Does the interlock override option work for the Earth switch?
No, the interlock override option is not available for the earth switch.
What conditions need to be fulfilled to operate the line earth switch?
The line isolator is open, no voltage in the line, and the VT MCB is ok.
I have tried to give a clear view on the topic interlock of circuit breaker, isolator, and earth switch. Thanks for your reading.
